IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Hemorrhage: Severe and fatal hemorrhages occurred with CABOMETYX. The incidence of Grade 3 to 5 hemorrhagic events was 5% in CABOMETYX patients in RCC, HCC, and DTC studies. Discontinue CABOMETYX for Grade 3 or 4 hemorrhage and prior to surgery as recommended. Do not administer CABOMETYX to patients who have a recent history of hemorrhage, including hemoptysis, hematemesis, or melena.
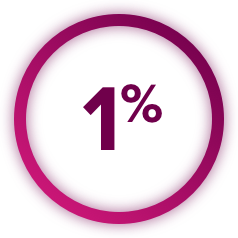
Perforations and Fistulas: Fistulas, including fatal cases, occurred in 1% of CABOMETYX patients. Gastrointestinal (GI) perforations, including fatal cases, occurred in 1% of CABOMETYX patients. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of fistulas and perforations, including abscess and sepsis. Discontinue CABOMETYX in patients who experience a Grade 4 fistula or a GI perforation.
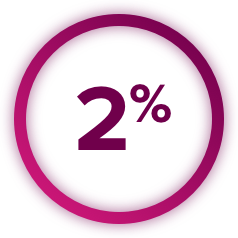
Thrombotic Events: CABOMETYX increased the risk of thrombotic events. Venous thromboembolism occurred in 7% (including 4% pulmonary embolism) and arterial thromboembolism in 2% of CABOMETYX patients. Fatal thrombotic events occurred in CABOMETYX patients. Discontinue CABOMETYX in patients who develop an acute myocardial infarction or serious arterial or venous thromboembolic events that require medical intervention.
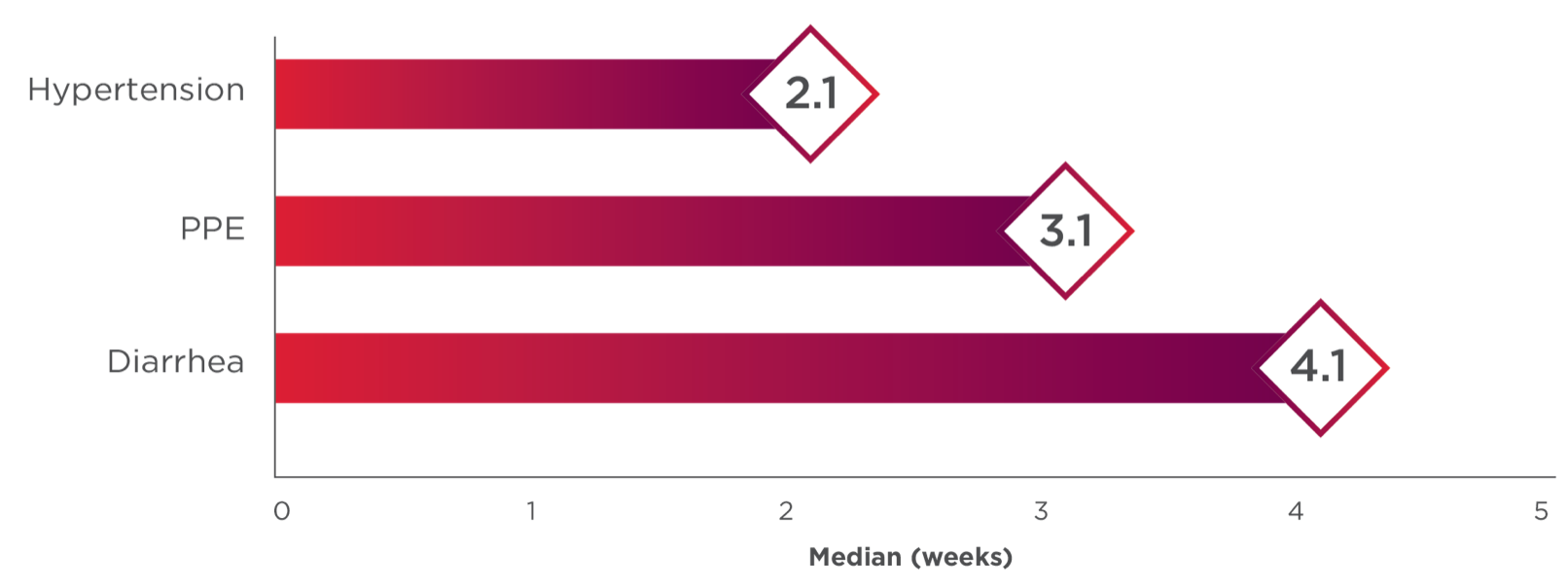
Hypertension and Hypertensive Crisis: CABOMETYX can cause hypertension, including hypertensive crisis. Hypertension was reported in 37% (16% Grade 3 and <1% Grade 4) of CABOMETYX patients. Do not initiate CABOMETYX in patients with uncontrolled hypertension. Monitor blood pressure regularly during CABOMETYX treatment. Withhold CABOMETYX for hypertension that is not adequately controlled with medical management; when controlled, resume at a reduced dose. Permanently discontinue CABOMETYX for severe hypertension that cannot be controlled with anti-hypertensive therapy or for hypertensive crisis.
Diarrhea: Diarrhea occurred in 62% of CABOMETYX patients. Grade 3 diarrhea occurred in 10% of CABOMETYX patients. Monitor and manage patients using antidiarrheals as indicated. Withhold CABOMETYX until improvement to ≤ Grade 1, resume at a reduced dose.
Palmar-Plantar Erythrodysesthesia (PPE): PPE occurred in 45% of CABOMETYX patients. Grade 3 PPE occurred in 13% of CABOMETYX patients. Withhold CABOMETYX until improvement to Grade 1 and resume at a reduced dose for intolerable Grade 2 PPE or Grade 3 PPE.
Proteinuria: Proteinuria was observed in 8% of CABOMETYX patients. Monitor urine protein regularly during CABOMETYX treatment. For Grade 2 or 3 proteinuria, withhold CABOMETYX until improvement to ≤ Grade 1 proteinuria; resume CABOMETYX at a reduced dose. Discontinue CABOMETYX in patients who develop nephrotic syndrome.
Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (ONJ): ONJ occurred in <1% of CABOMETYX patients. ONJ can manifest as jaw pain, osteomyelitis, osteitis, bone erosion, tooth or periodontal infection, toothache, gingival ulceration or erosion, persistent jaw pain, or slow healing of the mouth or jaw after dental surgery. Perform an oral examination prior to CABOMETYX initiation and periodically during treatment. Advise patients regarding good oral hygiene practices. Withhold CABOMETYX for at least 3 weeks prior to scheduled dental surgery or invasive dental procedures, if possible. Withhold CABOMETYX for development of ONJ until complete resolution, resume at a reduced dose.
Impaired Wound Healing: Wound complications occurred with CABOMETYX. Withhold CABOMETYX for at least 3 weeks prior to elective surgery. Do not administer CABOMETYX for at least 2 weeks after major surgery and until adequate wound healing. The safety of resumption of CABOMETYX after resolution of wound healing complications has not been established.
Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome (RPLS): RPLS, a syndrome of subcortical vasogenic edema diagnosed by characteristic findings on MRI, can occur with CABOMETYX. Evaluate for RPLS in patients presenting with seizures, headache, visual disturbances, confusion, or altered mental function. Discontinue CABOMETYX in patients who develop RPLS.
Thyroid Dysfunction: Thyroid dysfunction, primarily hypothyroidism, has been observed with CABOMETYX. Based on the safety population, thyroid dysfunction occurred in 19% of patients treated with CABOMETYX, including Grade 3 in 0.4% of patients.
Patients should be assessed for signs of thyroid dysfunction prior to the initiation of CABOMETYX and monitored for signs and symptoms of thyroid dysfunction during CABOMETYX treatment. Thyroid function testing and management of dysfunction should be performed as clinically indicated.
Hypocalcemia: CABOMETYX can cause hypocalcemia. Based on the safety population, hypocalcemia occurred in 13% of patients treated with CABOMETYX, including Grade 3 in 2% and Grade 4 in 1% of patients. Laboratory abnormality data were not collected in CABOSUN.
In COSMIC-311, hypocalcemia occurred in 36% of patients treated with CABOMETYX, including Grade 3 in 6% and Grade 4 in 3% of patients.
Monitor blood calcium levels and replace calcium as necessary during treatment. Withhold and resume at reduced dose upon recovery or permanently discontinue CABOMETYX depending on severity.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: CABOMETYX can cause fetal harm. Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to initiating CABOMETYX and advise them to use effective contraception during treatment and for 4 months after the last dose.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common (≥20%) adverse reactions are:
CABOMETYX as a single agent: diarrhea, fatigue, PPE, decreased appetite, hypertension, nausea, vomiting, weight decreased, and constipation.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors: If coadministration with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors cannot be avoided, reduce the CABOMETYX dosage. Avoid grapefruit or grapefruit juice.
Strong CYP3A4 Inducers: If coadministration with strong CYP3A4 inducers cannot be avoided, increase the CABOMETYX dosage. Avoid St. John’s wort.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Lactation: Advise women not to breastfeed during CABOMETYX treatment and for 4 months after the final dose.
Hepatic Impairment: In patients with moderate hepatic impairment, reduce the CABOMETYX dosage. Avoid CABOMETYX in patients with severe hepatic impairment.
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit www.FDA.gov/medwatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.