Mechanism of action
On This Page:
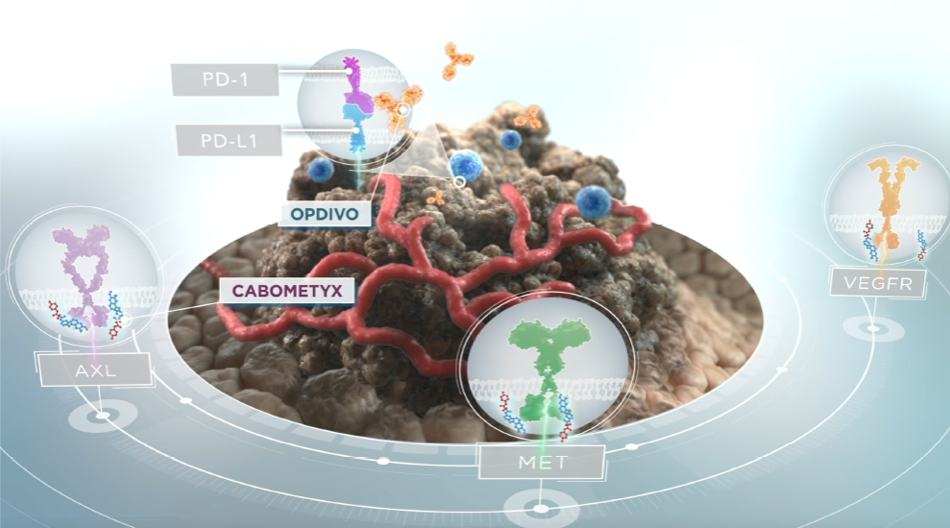
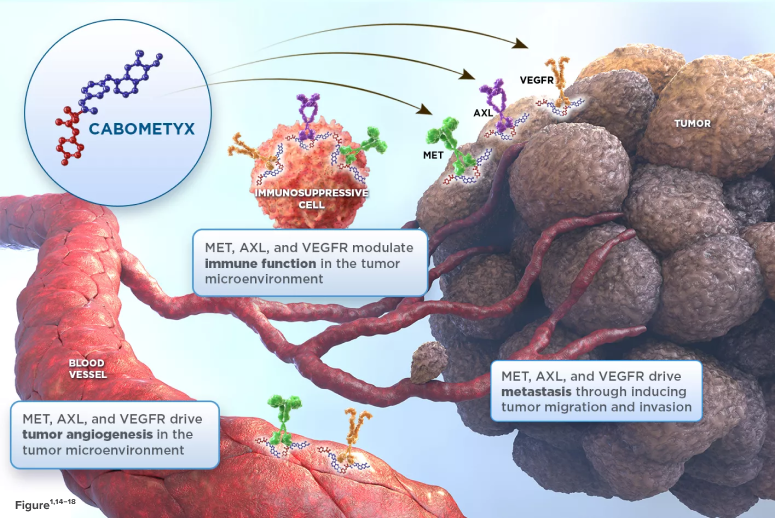
CABOMETYX® (cabozantinib) targets 3 key drivers of aRCC, HCC, DTC, and NET tumorigenesis—MET, AXL, and VEGFR1*†
- In aRCC, HCC, DTC, and NET tumor cells and cells of the tumor microenvironment, MET, AXL, and VEGF are overexpressed2-13
- These receptors are involved in normal and pathologic processes such as tumor angiogenesis, invasiveness, metastasis, and immunomodulation of the tumor microenvironment1,3,7,14-18
- *
-
Mechanism of action shown is based on in vitro biochemical and/or cellular assays. The clinical significance is unknown.1
- †
-
As seen in preclinical models; cabozantinib has also been shown to inhibit ROS1, TYRO3, MER, KIT, TRKB, FLT-3, and TIE-2.1
aRCC=advanced renal cell carcinoma; AXL=growth arrest-specific protein 6 receptor; DTC=differentiated thyroid cancer; FLT-3=FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3; HCC=hepatocellular carcinoma; KIT=KIT receptor tyrosine kinase; MET=mesenchymal epithelial transition kinase; NET=neuroendocrine tumors; RCC=renal cell carcinoma; ROS1=ROS1 receptor tyrosine kinase; TIE-2=tyrosine kinase with Ig and EGF homology domains-2; TKl=tyrosine kinase inhibitor; TRKB=tropomyosin receptor kinase B; TYRO3=TYRO3 protein tyrosine kinase; VEGF=vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR=vascular endothelial growth factor receptor.
References:
- CABOMETYX® (cabozantinib) Prescribing Information. Exelixis, Inc.
- Rankin EB, Fuh KC, Castellini L, et al. Direct regulation of GAS6/AXL signaling by HIF promotes renal metastasis through SRC and MET. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111(37):13373-13378.
- Zhou L, Liu X-D, Sun M, et al. Targeting MET and AXL overcomes resistance to sunitinib therapy in renal cell carcinoma. Oncogene. 2016;35(21):2687-2697. doi:10.1038/onc.2015.343.
- Kwilas AR, Ardiani A, Donahue RN, Aftab DT, Hodge JW. Dual effects of a targeted small-molecule inhibitor (cabozantinib) on immune-mediated killing of tumor cells and immune tumor microenvironment permissiveness when combined with a cancer vaccine. J Transl Med. 2014;12:294.
- Tannir NM, Schwab G, Grünwald V. Cabozantinib: an active novel multikinase inhibitor in renal cell carcinoma. Curr Oncol Rep. 2017;19(2):1-8. doi:10.1007/s11912-017-0566-9.
- Goyal L, Muzumdar MD, Zhu AX. Targeting the HGF/c-MET pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(9):2310-2318. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-2791.
- Abou-Alfa GK, Meyer T, Cheng AL, et al. Cabozantinib in patients with advanced and progressing hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(1):54-63. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1717002.
- Tsoti SM, Pinato DJ. AXL receptor tyrosine kinase expression as a prognostic marker and therapeutic target in neuroendocrine tumours. ESMO Open. 2018;3(suppl 2):A323. doi:10.1136/esmoopen-2018-EACR25.762.
- Zhu C, Wei Y, Wei X. AXL receptor tyrosine kinase as a promising anti-cancer approach: functions, molecular mechanisms and clinical applications. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):153. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-1090-3.
- Toffoli L, Ditsiou A, Gagliano T. Exploring emerging therapeutic targets and opportunities in neuroendocrine tumors: updates on receptor tyrosine kinases. Receptors. 2024;3(2):145-154.
- Maharjan CK, Ear PH, Tran CG, Howe JR, Chandrasekharan C, Quelle DE. Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13(20):5117. doi:10.3390/cancers13205117.
- Corti F, Brizzi MP, Amorosa V, et al. Assessing the safety and activity of cabozantinib combined with lanreotide in gastroenteropancreatic and thoracic neuroendocrine tumors: rationale and protocol of the phase II LOLA trial. BMC Cancer. 2023;23(1):908. doi:10.1186/s12885-023-11287-2.
- Chan JA, Faris JE, Murphy JE, et al. Phase II trial of cabozantinib in patients with carcinoid pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (pNET). J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(suppl 4):228. doi:10.1200/JCO.2017.35.4_suppl.228.
- Aguilera TA, Giaccia AJ. Molecular pathways: oncologic pathways and their role in T-cell exclusion and immune evasion—a new role for the AXL receptor tyrosine kinase. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23(12):2928-2933. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-17-0189.
- Aguilera TA, Rafat M, Castellini L, et al. Reprogramming the immunological microenvironment through radiation and targeting AXL. Nat Commun. 2016;7(13898):1-14. doi:10.1038/ncomms13898.
- Ilangumaran S, Villalobos-Hernandez A, Bobbala D, Ramanathan S. The hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)-MET receptor tyrosine kinase signaling pathway: diverse roles in modulating immune cell functions. Cytokine. 2016;82:125-139. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2015.12.013.
- Hubel J, Hieronymus T. HGF/MET-signaling contributes to immune regulation by modulating tolerogenic and motogenic properties of dendritic cells. Biomedicines. 2015;3(1):138-148. doi:10.3390/biomedicines3010138.
- Yang J, Yan J, Liu B. Targeting VEGF/VEGFR to modulate antitumor immunity. Front Immunol. 2018;9(978):1-9. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2018.00978.